
2020/01/30 - 2020/02/02
284位(同エリア359件中)
![]()
something like thatさん
- something like thatさんTOP
- 旅行記357冊
- クチコミ161件
- Q&A回答1件
- 356,878アクセス
- フォロワー24人
この旅行記のスケジュール
2020/01/30
この旅行記スケジュールを元に
3日目⑥ジュガンティーヤ前編
Hop-on Hop-off バス利用してのゴゾ島観光
クレンディのあとは本命のジュガンティーヤ
この旅行記では前半、博物館中心です。
-----------------------------
3日目①ゴゾ島へ
ゴゾ海峡フェリー Gozo Channel Ferry
フェリー乗り場(Cirkewwa、サークァ)
フェリー乗り場(Mgarr、ムガー)
ゴゾ島
Gozo
Għawdex
ヴィクトリア
Victoria
Ir-Rabat Għawdex
-----------------------------
3日目②ヴィクトリア・チタデル・ゴゾ大聖堂
ヴィクトリア
Victoria
Ir-Rabat Għawdex
チタデラ(チタデル)
Cittadella
ゴゾ大聖堂
Il-Katidral ta' Għawdex
Cathedral Museum
-----------------------------
3日目③アズール・ウィンドウ
アズール・ウィンドウ
It-Tieqa tad-Dwejra
=Blue Hole/Blue Window
※現在は2017年の嵐で崩れて穴を見ることはできない。
-----------------------------
3日目④タ・ピーヌ聖堂
タ・ピーヌ聖堂
Bażilika Tal-Madonna Ta' Pinu Mill Gharb
-----------------------------
3日目⑤クレンディ
クレンディ
Xlendi
-----------------------------
3日目⑥ジュガンティーヤ前編
ジュガンティーヤ博物館
Ggantija Museum
-----------------------------
3日目⑦ジュガンティーヤ後編
ジュガンティーヤ
it-Tempji tal-Ġgantija
-----------------------------
3日目⑧タ・コーラ風車とラムラビーチ
タ・コーラ風車
Il-Mitħna ta' Kola
ラムラビーチ
Ramla Beach
ir-Ramla l-Ħamra
赤茶色の砂浜ビーチ
-----------------------------
3日目⑨ヴァレッタへの帰途
- 旅行の満足度
- 4.5
- 同行者
- 一人旅
- 交通手段
- 徒歩
- 旅行の手配内容
- 個別手配
-
ジュガンティーヤ博物館
Ġgantija Museum
バスを降りてビジターセンター入り口へ。
14:52
以下Wikiからの転載。
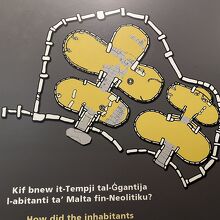
ジュガンティーヤ(Ġgantija)は、地中海に浮かぶゴゾ島にある新石器時代の巨石神殿複合体である。その名称はマルタ語で「巨人の塔」を意味する。マルタにある巨石神殿群の中でも最古のものとされている。ジュガンティーヤの2つの神殿は新石器時代(紀元前3600年から2500年ごろ)に建設されたもので、5500年前からあり、世界的にも最古の宗教施設の1つと言える。周辺の類似の構造物と共に「マルタの巨石神殿群」として世界遺産に登録されている。
この神殿は豊穣神崇拝の場だったと見られている。考古学者らはこの遺跡で見つかった多数の小像や彫刻がその信仰と結びついていると考えている。ゴゾ島の伝承によれば、巨人がこれらの神殿を建て、礼拝所として使ったという[1]。
構造など
ジュガンティーヤ神殿はシャーラ高原の端にあり、南東に面している。
この巨石記念物は実際には2つの神殿で構成されており、境界をなしている壁の中に2つが隣接して建っている。南側の大きな神殿の方が古く、紀元前3600年ごろまで遡る。また、保存状態もこちらの方がよい。5つの大きなアプスがあり、石と石の間の隙間にかつて漆喰で壁面を覆っていた痕跡が残っている。
ジュガンティーヤ神殿
内部は瓦礫で埋まっていたが、壁の内面を覆っていたブロックの位置から、全体としてクローバー形の建物だったことがわかっている。つまり、中心となる通路に半円形のアプスがいくつか繋がった建物である。考古学者らは、アプスには元々屋根がかかっていたと信じている。マルタの原住民には金属器がまだ入手できない時代、車輪ももたらされていない時代に建てられたと考えると、非常に印象的である。小さな球形の石が見つかっており、神殿建設時に巨石を運ぶ際のころとして使われたと見られている。
マルタの他の巨石神殿と同様、ジュガンティーヤ神殿も南東に面している。南の神殿は6メートルの高さがある。入口の巨石にはへこみがあり、ここが施設に入る際の清めの儀式の場所だったという説もある。5つのアプスにはそれぞれ祭壇がある。動物の骨が見つかっており、動物を生贄として捧げたのではないかと言われている。
発掘とその後
ゴゾ島の住民や旅行者は古くからこの神殿の存在を知っていた。発掘調査が行われる以前の18世紀後半、Jean-Pierre Hoüel は現地人の話に基づいてかなり正確な平面図を描いている。1827年、ゴゾ島の州副知事 John Otto Bayer はこの遺跡の瓦礫を撤去させた。なお、このとき撤去したものについては適切な調査が行われていない。幸運にも瓦礫撤去の1、2年前にドイツ人画家 Brochtorff がこの遺跡の絵を描いており、撤去前の唯一の記録となっている。
この土地は私有地だったが、1933年に政府が公益のために収用した。1933年、1936年、1949年、1956-57年、1958-59年に考古学的調査が行われた。
1980年、ジュガンティーヤ神殿は世界遺産に登録された。1992年、マルタの5つの巨石神殿もそれに加えることが決まった。そのため登録名称が「マルタの巨石神殿群 (The Megalithic Temples of Malta)」に変更された。ジュガンディーヤ神殿 城・宮殿
-
ジュガンティーヤ博物館
Ġgantija Museum
印象的な鳥の模様が刻まれた破片。 -
ジュガンティーヤ博物館
Ġgantija Museum
印象的な鳥の模様が刻まれた破片(拡大)。 -
ジュガンティーヤ博物館
Ġgantija Museum
A Unique pottery sherd from Ġgantija
This piece of pottery was discovered in the front terrace wall at Ġgantija in 1954 and dates back to around 3100-2400 BC. Originally, it formed part of a bowl with small lugs. Its decoration was incised after firing.
In creating this decoration, the 'temple' people seem to have been inspired by their daily life experience and contact with nature from which they borrowed some of their motifs.
incise:刻む、彫刻する
motif:モチーフ、(デザインなどの)基調、飾り、模様、文字、デコレーション -
ジュガンティーヤ博物館
Ġgantija Museum
plaster fragments(しっくいの付いた破片) -
ジュガンティーヤ博物館
Ġgantija Museum
These plaster fragments were discovered in the South Temple at Ġgantija. These rare finds indicate that the rough Coralline Limestone walls may have been covered in plaster to give them a smooth finish and then painted in red ochre.
Ochres are natural pigments that have been used for painting throughout history. Fragments of these natural pigments have been found in temples, on artefacts and even on human remains. Contrary to popular belief, the local geology could have provided the primary source of these pigments. Recent studies have indetified various potential sources of ochre on the Maltese islands.
Coralline:サンゴ状動物(珊瑚質の)
Limestone:石灰岩
ochre(ocher):黄土色 -
ジュガンティーヤ博物館
Ġgantija Museum
器の縁(ふち)の一部(上)と牛の角の一部(下) -
ジュガンティーヤ博物館
Ġgantija Museum
Part of a Bull's horn found beneath the threshold of the South Temple at Ġgantija.
Rim of a Bowl discoverd in the Ġgantija Temples. Numerous fragments of clay vessels have been discovered in the Megalithic Temples.
threshold:敷居、入り口
Numerous:多数の、おびただしい数の -
ジュガンティーヤ博物館
Ġgantija Museum
Two Limestone heads
2つの石灰岩でできた頭 -
ジュガンティーヤ博物館
Ġgantija Museum
Two Limestone heads found at the back of one of the rooms of the Ġgantija South Temple. -
ジュガンティーヤ博物館
Ġgantija Museum
Conical stone
円錐形の石 -
ジュガンティーヤ博物館
Ġgantija Museum
Conical stone originally discovered in one of the outer rooms of the Ġgantija South Temple. -
ジュガンティーヤ博物館
Ġgantija Museum
Double-figure stone statuette
2体の石の小像 -
ジュガンティーヤ博物館
Ġgantija Museum
Double-figure stone statuette. This is the most complete and remarkable sculpture from the Xagħra Circle, depicting a miniature, highly detailed seated pair of corpulent figures.
statuette:小像
corpulent:でぶでぶ太った、肥満した -
ジュガンティーヤ博物館
Ġgantija Museum
This wooden reconstruction shows how furniture was probably constructed out of timber framework. This statuette and the sleeping lady from the Ħal Saflieni Hypogeum are our best evidence for furniture used in the Neolithic. -
ジュガンティーヤ博物館
Ġgantija Museum
Stylized human and animal figurines founds together in a heap on the floor at the Xagħra Circle. These are carved in limestone and it is likely that they were originally bound or wrapped together with a perishable material such as animal skin.
figurine:(金属・陶土などで作った)小立像、人形
perishable:腐敗しやすい -
ジュガンティーヤ博物館
Ġgantija Museum
Seated clay figurines and clay representation of a snail with a human head(一番右下に陳列されているものを指しているみたい) from the Xagħra Circle. -
ジュガンティーヤ博物館
Ġgantija Museum -
ジュガンティーヤ博物館
Ġgantija Museum
牛の爪先の骨に人間の顔を掘って加工したもの。 -
ジュガンティーヤ博物館
Ġgantija Museum -
ジュガンティーヤ博物館
Ġgantija Museum
When individuals were buried, they were accompanied by some belongings. These items were discovered in the oldest tomb within the Xagħra Circle. It dated to the Żebbuġ phase(c.4100BC) and included a rare example of
1. Statue Menhir - a stone block with a carving of a stylized human
2. Faceshell necklaces
3. Bone necklace
4. Typical Żebbuġ phase pottery
5. Axe-pendants
6. Large triton shell
Menhir:メンヒル
the Żebbuġ phase:4100?3800 BC -
ジュガンティーヤ博物館
Ġgantija Museum -
ジュガンティーヤ博物館
Ġgantija Museum -
ジュガンティーヤ博物館
Ġgantija Museum
Rectangular stone trough found at the Xagħra Circle
trough: (家畜の飼料・水などを入れる細長い)かいばおけ、槽(ふね) -
ジュガンティーヤ博物館
Ġgantija Museum -
ジュガンティーヤ博物館
Ġgantija Museum
SKULL found at the Xagħra Circle. This is the skull of a woman which was studied by forensic experts in order to recreate what she looked like when she was alive in the Neolithic.
forensic:法医学の
Neolithic:新石器時代
15:08
この旅行記のタグ
利用規約に違反している投稿は、報告する事ができます。
コメントを投稿する前に
十分に確認の上、ご投稿ください。 コメントの内容は攻撃的ではなく、相手の気持ちに寄り添ったものになっていますか?
サイト共通ガイドライン(利用上のお願い)報道機関・マスメディアの方へ 画像提供などに関するお問い合わせは、専用のお問い合わせフォームからお願いいたします。
something like thatさんの関連旅行記
この旅行で行ったスポット
ゴゾ島(マルタ) の旅行記
旅の計画・記録
マイルに交換できるフォートラベルポイントが貯まる
フォートラベルポイントって?


![ジュガンティーヤ博物館<br />Ġgantija Museum<br /><br />バスを降りてビジターセンター入り口へ。<br />14:52<br /><br />以下Wikiからの転載。<br />ジュガンティーヤ(Ġgantija)は、地中海に浮かぶゴゾ島にある新石器時代の巨石神殿複合体である。その名称はマルタ語で「巨人の塔」を意味する。マルタにある巨石神殿群の中でも最古のものとされている。ジュガンティーヤの2つの神殿は新石器時代(紀元前3600年から2500年ごろ)に建設されたもので、5500年前からあり、世界的にも最古の宗教施設の1つと言える。周辺の類似の構造物と共に「マルタの巨石神殿群」として世界遺産に登録されている。<br /><br />この神殿は豊穣神崇拝の場だったと見られている。考古学者らはこの遺跡で見つかった多数の小像や彫刻がその信仰と結びついていると考えている。ゴゾ島の伝承によれば、巨人がこれらの神殿を建て、礼拝所として使ったという[1]。<br /><br />構造など<br />ジュガンティーヤ神殿はシャーラ高原の端にあり、南東に面している。<br /><br />この巨石記念物は実際には2つの神殿で構成されており、境界をなしている壁の中に2つが隣接して建っている。南側の大きな神殿の方が古く、紀元前3600年ごろまで遡る。また、保存状態もこちらの方がよい。5つの大きなアプスがあり、石と石の間の隙間にかつて漆喰で壁面を覆っていた痕跡が残っている。<br /><br />ジュガンティーヤ神殿<br />内部は瓦礫で埋まっていたが、壁の内面を覆っていたブロックの位置から、全体としてクローバー形の建物だったことがわかっている。つまり、中心となる通路に半円形のアプスがいくつか繋がった建物である。考古学者らは、アプスには元々屋根がかかっていたと信じている。マルタの原住民には金属器がまだ入手できない時代、車輪ももたらされていない時代に建てられたと考えると、非常に印象的である。小さな球形の石が見つかっており、神殿建設時に巨石を運ぶ際のころとして使われたと見られている。<br /> マルタの他の巨石神殿と同様、ジュガンティーヤ神殿も南東に面している。南の神殿は6メートルの高さがある。入口の巨石にはへこみがあり、ここが施設に入る際の清めの儀式の場所だったという説もある。5つのアプスにはそれぞれ祭壇がある。動物の骨が見つかっており、動物を生贄として捧げたのではないかと言われている。<br /><br />発掘とその後<br />ゴゾ島の住民や旅行者は古くからこの神殿の存在を知っていた。発掘調査が行われる以前の18世紀後半、Jean-Pierre Hoüel は現地人の話に基づいてかなり正確な平面図を描いている。1827年、ゴゾ島の州副知事 John Otto Bayer はこの遺跡の瓦礫を撤去させた。なお、このとき撤去したものについては適切な調査が行われていない。幸運にも瓦礫撤去の1、2年前にドイツ人画家 Brochtorff がこの遺跡の絵を描いており、撤去前の唯一の記録となっている。<br />この土地は私有地だったが、1933年に政府が公益のために収用した。1933年、1936年、1949年、1956-57年、1958-59年に考古学的調査が行われた。<br />1980年、ジュガンティーヤ神殿は世界遺産に登録された。1992年、マルタの5つの巨石神殿もそれに加えることが決まった。そのため登録名称が「マルタの巨石神殿群 (The Megalithic Temples of Malta)」に変更された。](https://cdn.4travel.jp/img/thumbnails/imk/travelogue_pict/72/52/37/650x_72523752.jpg?updated_at=1647179868)










































0
26